Using the Critical Path Method (CPM) in Project Management: A Guide to Get Started
Developed in the 1950s, the Critical Path Method (CPM) was created to streamline the planning and execution of complex projects. Its main function is to identif...
Developed in the 1950s, the Critical Path Method (CPM) was created to streamline the planning and execution of complex projects. Its main function is to identify the longest sequence of dependent tasks. In this article, we'll teach you how CPM works, why to use it, and how to get started.

📍 What is the Critical Path Method (CPM)?
In a nutshell, the Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique used to plan and control complex projects. At a glance, that doesn’t seem revolutionary, but there’s a catch.
The method identifies the longest sequence of dependent tasks in a project, the critical path, which determines the project's minimum completion time.
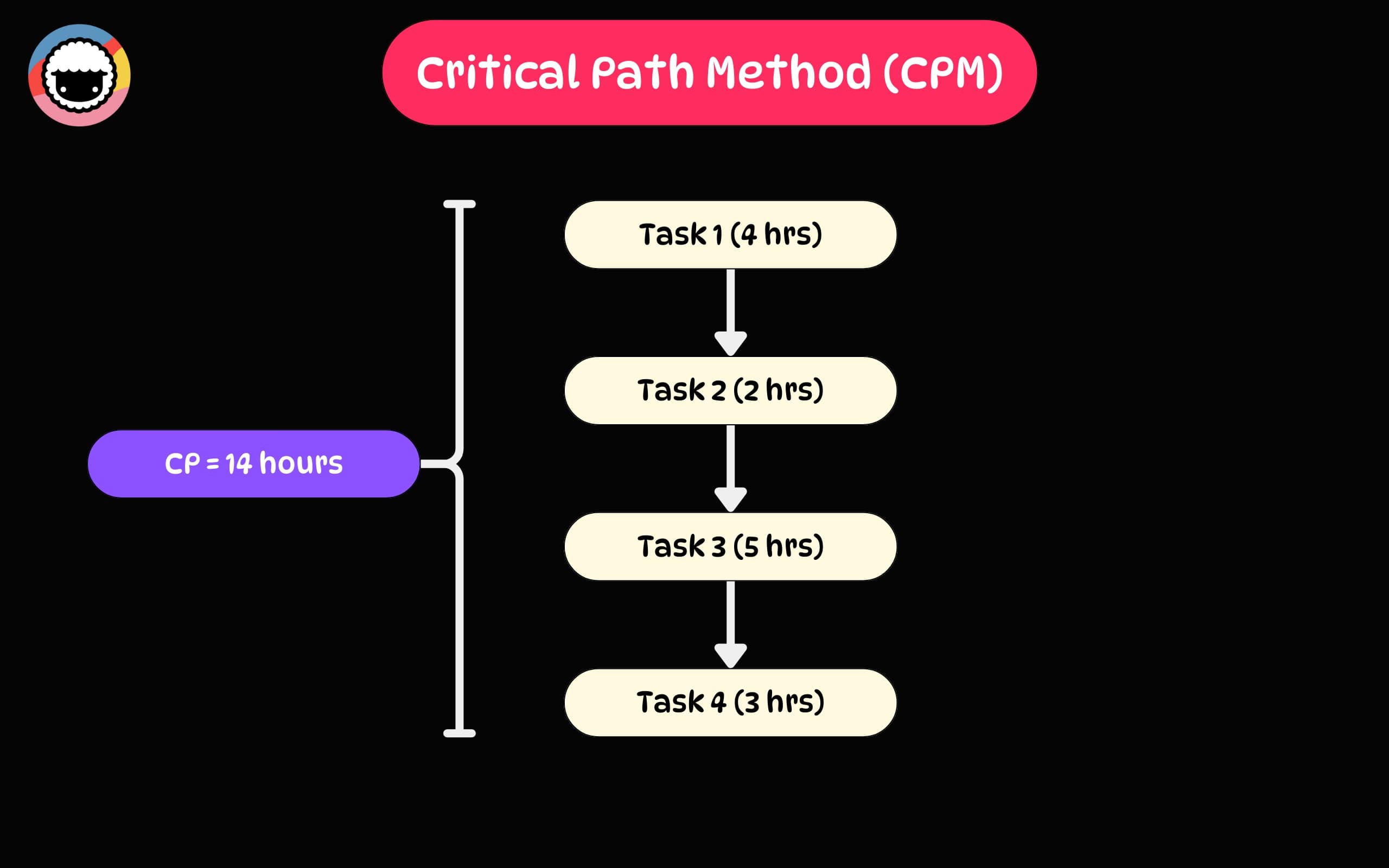
It's like the main power line in a circuit. If it’s interrupted, the lights go out on the whole system. Every other connection relies on this main path for energy and flow.
Unlike other project management methods, CPM focuses on task dependencies and timing. It also identifies potential bottlenecks and places where delays could impact the entire project.
💡 Check our project management basics guide if you’re just getting started.
🧩 Key Concepts of the Critical Path Method
The Critical Path Method breaks down into several core components.
Activities and Dependencies
Activities are the individual tasks that make up a project. Each task has a specific duration, which, in turn, determines resource allocation and project completion times.
Dependencies link these tasks in a sequence. They specify the exact order for task execution, which helps prevent any conflicts and keeps the project on track.
Together, activities and dependencies form the project’s framework.
Activity Durations
Activity durations refer to the time needed to complete each task.
Simple, right?
But accurate estimates are key in CPM. Short durations cause resource gaps and delays, while long ones waste resources and inflate costs, so it’s important to get these right from the start.
Precise durations are your key to a smooth project flow. Keep an eye on these durations and be ready to adjust them, so you can adapt to any surprises or changes along the way.
Critical Path
The critical path is the longest sequence of activities in a project.
So, why is it so important? Because it determines the shortest time possible to complete the project. It also highlights tasks that need immediate attention to avoid delays.
Changes to the critical path directly impact the end date. Staying on top of this path helps you prioritize resources and efforts, keeping the project on track and avoiding unnecessary setbacks.
Float/Slack
Float or slack is the time a task can be delayed without impacting the completion date.
There are two types: total float and free float. Total float refers to delay time without affecting the project's end date. Free float allows delay without impacting subsequent tasks.
Network Diagram
A network diagram visually represents the sequence of project activities. It also shows how tasks are interrelated and dependent, which helps spot potential bottlenecks and improve task coordination.
The layout provides a clear visual path from start to finish — nodes represent activities, arrows illustrate dependencies, and various colors distinguish different types of activities or milestones.
⚡ Benefits of Using the Critical Path Method
Better, Faster Decisions
Here's the deal: bad decisions sink almost half of failed projects. Yep, that's a whopping 47%.
CPM highlights essential tasks for project teams to focus on. It also shows the impact of potential delays on the project timeline. This, in turn, leads to faster and more informed decisions.
Clear Roles, Stronger Team
Research shows that teams working well together are 50% more productive.
CPM clearly outlines roles and responsibilities for each team member. It specifies who does what and when, which helps reduce confusion and overlap.
The extra visibility ensures every team member knows their part to play. Team members own their tasks and results, which drives improved performance and accountability.
Accurate Time Estimates
The Project Management Institute reports that almost half of projects don't finish on schedule.
CPM uses task dependencies to guide accurate timeline estimates and pinpoint critical tasks. This minimizes the risk of overruns and enhances overall scheduling accuracy. But that’s not all.
CPM often incporporates historical data to make better time estimates for each task. By analyzing past project durations, you can quickly adjust to unforeseen changes and improve future project timelines.
⚙️ How to Implement CPM in Your Project
Enough theory — let’s talk execution. Implementing CPM is about getting results. You need a clear plan to manage your tasks and timelines effectively. Here’s how to get started.
Step 1: Identify All Tasks
Kick things off by jotting down every task your project needs.
Capture the full scope, so nothing slips through the cracks. Define each task clearly to avoid any confusion later. Don't guess — get input from your team to cover all bases.
This is the foundation your whole plan rests on, so make it solid.
✅ List out tasks for every phase of your project.
✅ Get your team's input to make sure you've got everything.
✅ Be clear and specific about what each task involves.
✅ Double-check to catch any missed tasks or subtasks.
✅ Arrange tasks in a logical order so you can track them easily.
Step 2: Determine Task Dependencies
In the second phase, you need to figure out how tasks are connected and what needs to happen first. This will help you understand the flow and order of the project.
Determine which tasks rely on others to kick off or finish. Talk to your team to map out these dependencies accurately. Knowing this will prevent roadblocks and keep everything moving.
✅ Identify what tasks must be done before others can start.
✅ Discuss with your team to pinpoint these connections.
✅ Document the sequence and flow of tasks clearly.
✅ Use visuals like charts or diagrams to make dependencies easy to see.
✅ Keep an eye out for any potential bottlenecks.
Step 3: Estimate Task Durations
Next, guess how long each task will take, but make it realistic. Tap into the expertise of your team to get accurate estimates. Consider past projects or similar tasks to guide your guesses.
This step is crucial for setting a reliable projects chedule; it's better to underpromise and overdeliver.
✅ Collaborate with your team to get time estimates.
✅ Look at historical data from similar projects.
✅ Factor in potential delays or challenges.
✅ Be realistic, but also leave room for flexibility.
✅ Review and adjust estimates regularly as the project progresses.
🐑 Pro Tip: Taskade lets youbuild Custom AI agents tailored to project needs. You can enven train your agents on records of past projects to enhance their predictive capabilities.
F
First, go to your Taskade workspace and navigate to the Agents tab.
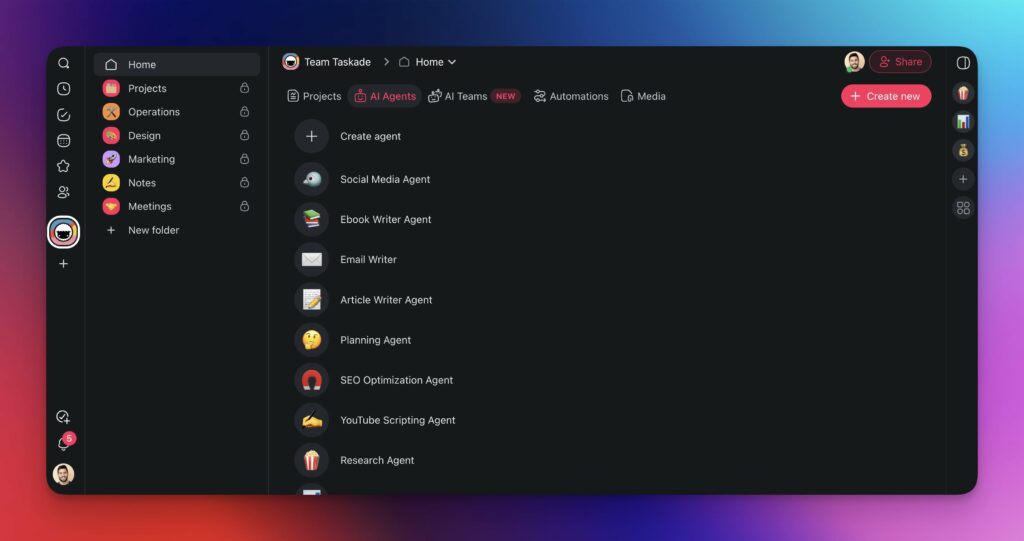
Next, click ➕ Create agent and ✨ Generate with AI.
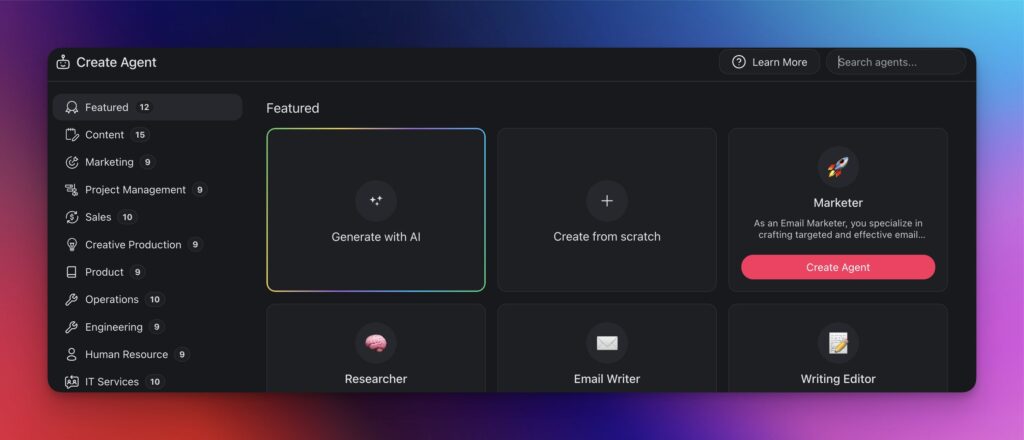
Finally, describe the purpose of your agent. Here's a prompt we used to create our CPM agent.

Next, go to the Knowledge tab on the left and add some documents for the agent to learn from.
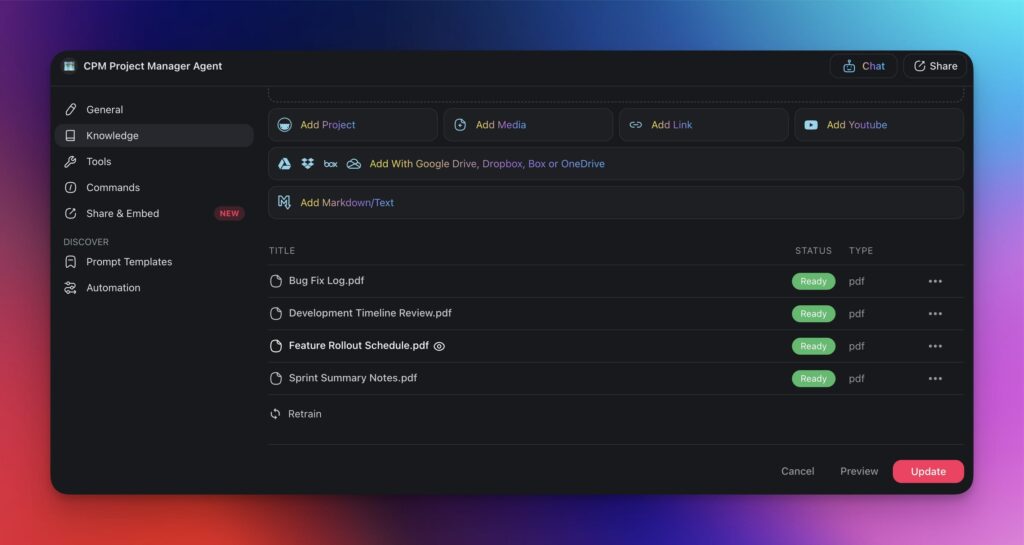
Now, the next time you kick off a new project, choose your agent from the sidebar on the left and ask it to generate task duration estimates based on historical data. It's that simple!
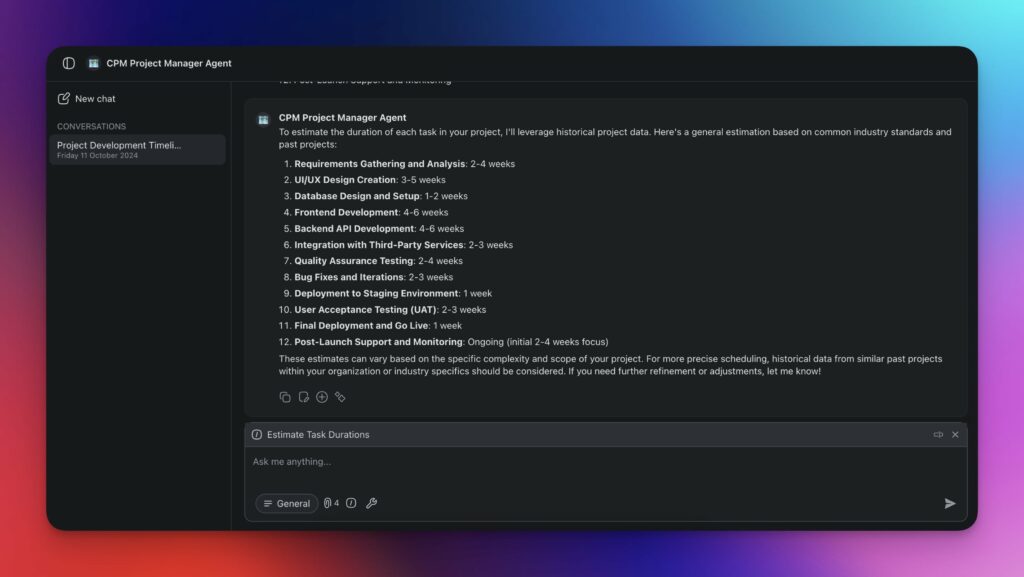
Step 4: Create a Network Diagram
It’s time to bring your project to life visually!
Draw up a network diagram to map out tasks and their dependencies. The diagram shows the flow and order of tasks, which will make it a tad easier to grasp the project structure.
You can go the manual route with a whiteboard for hands-on creativity. Or, try software for a polished and editable format. Either way, keep the diagram up to date throughout the project.
✅ Collaborate with your team to get time estimates.
✅ Look at historical data from similar projects.
✅ Factor in potential delays or challenges.
✅ Be realistic, but also leave room for flexibility.
✅ Review and adjust estimates regularly as the project progresses.
Step 5: Calculate the Critical Path
This is where things get interesting.
As you probably remember, the critical path is the longest stretch of dependent tasks from start to finish. It indicates the shortest time the project can be completed.
For example, a house build might follow a 29-day critical path: foundation (5 days), frame (10 days), plumbing/electrical (7 days), drywall (3 days), and interior finishing (4 days).
✅ Analyze tasks to find the longest chain of dependencies.
✅ Pay attention to tasks on this path as they are crucial.
✅ Use project management software for accurate calculations.
✅ Monitor these tasks closely to avoid delays.
✅ Adjust resources if needed to keep the critical path on track.
🤹 Practical Applications of CPM
Let’s explore how the Critical Path Method performs in some real-world challenges.
Construction Projects
With sequential tasks that depend on one another, construction is a perfect environment for CPM.
A typical construction project might include phases like site preparation, foundation laying, framing, wiring, plumbing, and roofing. You can’t start one, before finishing the previous one.
For example, you can't install the plumbing before the walls are up, and you can't start the interior finishes until all rough-ins are complete. Any delay in acquiring permits or inspections can halt progress.
CPM helps identify any dependencies and decide which tasks are critical and which have a bit of slack.
It ensures heavy machinery is allocated properly, helps schedule labor crews and coordinate delivery of materials, and even accounts for weather-related disruptions.
Software Development
Software development projects are no different.
A typical software project includes phases like requirements gathering, design, coding, testing, and deployment. Each phase builds on the last and usually can’t be can’t be skipped or reshuffled.
You can't start integration testing before the modules are coded and unit-tested. Similarly, missing out on the design phase may result in an architecture that doesn't support scalability.
Any delay in client sign-offs or resource allocation can disrupt timelines.
While Agile methodologies allow for more flexibility and adaptation, some core phases remain non-negotiable, and CPM can be instrumental in identifying critical tasks and dependencies.
Manufacturing Processes
Did you know that Henry Ford's assembly lines cut down car production time from 12 to just 2.5 hours?
In manufacturing, each phase—sourcing materials, production, assembly, quality check, and packaging—must flow seamlessly to ensure peak performance.
Assembly can't kick off without all components ready, and packaging waits on thorough quality inspections. A hiccup in supplies or machinery can throw a wrench in the works.
CPM helps pinpoint essential tasks and potential logjams, optimizing equipment usage, and synchronizing labor and material schedules. It keeps everything on track, minimizing hiccups.
👋 Wrapping Up: The Impact of the Critical Path Method on Successful Project Delivery
As project demands continue to evolve, integrating the Critical Path Method (CPM) into your project management practices is essential. CPM offers a structured approach that enhances focus, defines priorities, and provides a clear roadmap for project progression.
Before you go, here are a few key highlights from the article:
⭐ The Critical Path Method (CPM) was developed in the late 1950s.
⭐ Project managers use CPM to maintain control and ensure projects stay on track.
⭐ CPM's core principle is to identify the longest sequence of dependent tasks.
⭐ The method breaks down task dependencies and their effects on project timelines.
⭐ It provides accurate estimates for project completion and helps allocate resources.
⭐ The method is highly adaptable and can be applied to various industries.
⭐ CPM often employs network diagrams to visually represent tasks and their dependencies.
⭐ The method supports informed decision-making by clarifying the impact of task delays.
⭐ While Gantt charts outline resources, CPM focuses on the task sequence.
But wait, there's more!
What if we told you that you can embrace all the benefits of CPM without the manual work?
Taskade is an AI-powered project management and collaboration platform that takes the legwork out of project planning, management, and execution. It’s your digital sidekick that keeps work on track.
Sign up for Taskade AI, and stay on top of your game! 👈
🤖 Custom AI Agents: Create intelligent, autonomous AI assistants to support your project management needs around the clock. Customize agents with knowledge and skills, and connect them to your favorite tools and platforms.
👥 AI Teams: Organize your AI agents into specialized groups based on their skills and purpose. Tap into the collective expertise of AI teams to boost productivity and achieve superior outcomes right inside your workspace.
⚡️ Smart Automations: Enhance your workflow with AI-powered automation using ready-made templates. Customize triggers and actions to connect with apps like Gmail, HubSpot, and more.
🪐 One App to Rule Them All: Streamline your project workflow by managing everything in one place. Consolidate all your tasks, notes, tools, and docs in a single platform. Keep everything and everyone aligned without any hassle.
And much more...